Cont ...
Operations Master Roles (Flexible Single Master Operations - FSMO)
Operations master roles (also known as flexible single master operations, or FSMO) are special roles assigned to one or more domain controllers in an Active Directory domain.
Active Directory supports multi-master replication of the directory data store between all domain controllers in the domain. Hence all domain
controllers in a domain are considered essentially peers. But,
replication conflicts do occur during Active Directory replication. Some
operations that occur on a Windows Server 2003 Active Directory could
be harmful if conflicts were to occur. In the case of these operations,
Windows 2003 reverts to using a single-master model. This means that a single Domain Controller
on the network takes responsibility for performing a specific task and
these Domain Controllers are called as the Operations Master.
There are five Operation Master Roles and two of them are Forest level roles and three of them are Domain Level roles. Following table lists the Operation Master Roles and their scope.
Operations Master
|
Scope
|
Schema Master
|
Forest wide
|
Domain Naming Master
|
Forest wide
|
Primary Domain Controller (PDC) Emulator
|
Domain wide
|
Relative Identifier (RID) Master
|
Domain wide
|
Infrastructure Master
|
Domain wide
|
Schema Master
Active Directory schema defines what can exist within the directory. Managing the process of updating it with new objects and attributes should be a closely monitored process. There is only a single read/write copy of the schema on your Windows Server 2003 network, stored on the Schema Master.
The domain controller assigned the schema master role controls all updates and modifications to the schema. To update the schema of a forest, you must have access to the schema master.
There only a single Schema Master in the entire forest at any time.
Domain Naming Master
All objects within
AD must be unique. We cannot create two objects in a container with the
same name, and the distinguished names all of all objects must be
unique. Domain Naming Master ensures that new domains added to your Windows Server 2003 forest have unique names.
There only a single Domain Naming Master in the entire forest at any time.
PDC (Primary Domain Controller) Emulator
The PDC emulator
services network clients that do not have Active Directory client
software installed, and it replicates directory changes to any Microsoft Windows NT backup domain controllers (BDCs) in the domain.
Even the domain is operating at Windows 2003 functional level, PDC Emulator is required to perform certain tasks.
The PDC emulator receives preferential replication of password changes performed by other domain controllers in the domain.
If a password was recently changed, that change takes time to replicate to every domain controller in the domain. If a logon authentication fails at another domain controller due to a bad password, that domain controller forwards the authentication request to the PDC emulator before rejecting the logon attempt.
There is only a single PDC Emulator per domain.
Relative ID (RID) Master
A Security
Principal is an Active Directory object that can be assigned permissions
within a Windows Server 2003 network. Examples for Security Principal
objects are users, groups, and computers. Each Security Principal is
assigned a Security Identifier (SID) so it can be identified.
A Security
Identifier (SID) is made up of two components. The first component, the
domain SID, is common to all security principals in a domain. The
uniqueness in SID comes from the addition of a second number, the
Relative Identifier (RID). The RID is assigned from a pool of RIDs
stored at each Domain Controller. The RIDs in this pool are assigned to each Domain Controller by the RID Master.
The format of SID follows this pattern: S-R-IA-SA-SA-RID.
• S represents a SID identifier.
• R represents the Revision. All SIDs generated by Windows use a revision level of 1.
• IA represents the issuing authority.
• SA represents a sub-authority, and
• RID is the Relative ID
A typical user SID looks like this: S-1-5-21-1683771067-1221355100-624655392-1001.
RIDs are assigned
to each DC in blocks of 500 RIDs. When the block of RIDs is exhausted,
the DC requests another block from the RID Master. To ensure uniqueness,
the RID Master keeps track of which RID blocks have been assigned.
If the RID pool on
a DC is exhausted and the RID Master is not available, you will not be
able to create Security Principals (Example: a user) on that server.
There is only a single RID Master per domain.
Infrastructure Master
The domain controller
assigned the infrastructure master role is responsible for updating the
group-to-user references whenever the members of groups are renamed or
changed.
There is a single Infrastructure Master per domain.How to transfer Operations Master roles (FSMO) to another Domain Controller
How to transfer Domain wide Operations Master (FSMO) to another Domain Controller
Follow these steps to transfer the domain wide operations master from one domain controller to another domain controller.
• Open “Active
Directory Users and Computers” MMC snap-in. (Start > Programs >
Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers)
• Right click the domain to which you want to transfer the role, select Operations Masters" from the popup menu.
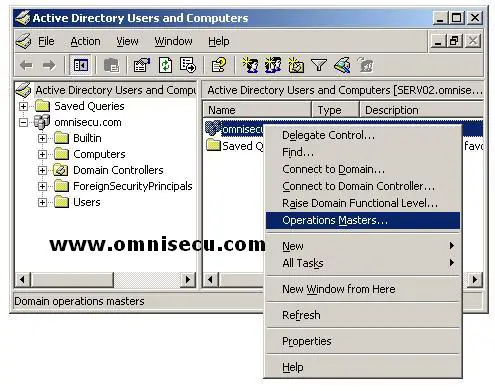
• There are three tabs in the “Operation Masters” dialog
box, showing three domain wide “Operations Masters” role (RID
Operations master, PDC Operations master and Infrastructure Operations
master).
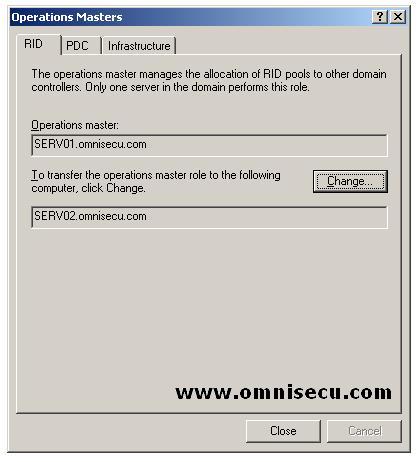
• To transfer the role to this domain controller from the domain controller displayed on the “Operations Master” text field, click the “Change” button.
How to transfer the Forest wide Operations Master (FSMO) roles to another domain controller
To transfer the Domain Naming Master, follow these steps.
• Open the "Active Directory Domains and Trusts" MMC snap-in (Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts).
• Right click the “Active Directory Domains And Trusts” node, and then click Operations Master.
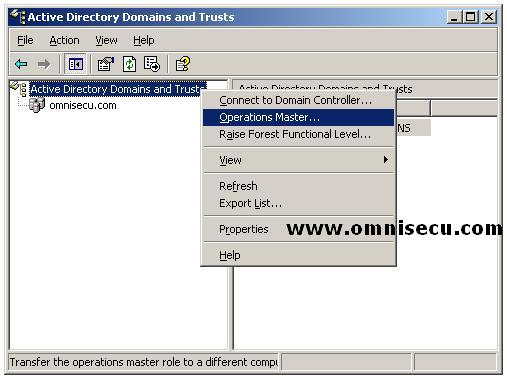
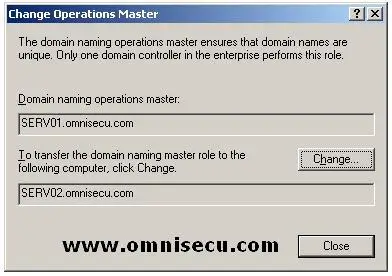
• Click the “Change” button to change the “Domain Naming operations master" (FSMO) role to the new Domain Controller.
To transfer the Schema Operations Master Role, follow these steps.
• Open “Active Directory Schema” snap-in, by using MMC (Microsoft Management Console) Add/Remove snap-in menu (To open MMC (Microsoft Management Console), open the run dialog from Windows Start menu, type mmc and hit ENTER).
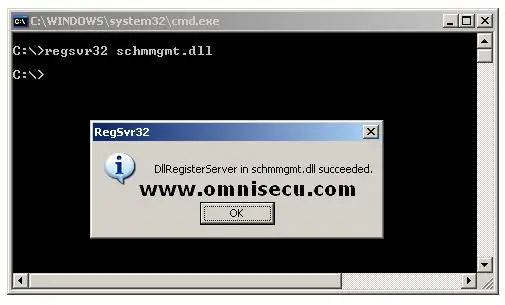
Note: You may not see "Active Directory Schema" snap-in in your MMC "Add/Remove snap-in" menu, unless you register the related dll file. Follow these steps to complete it. Run Command Prompt by opening "run" dialog from Windows start menu, type "Cmd" and hit ENTER. Type regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll. A message box informs you that the registration succeeded as shown below (make sure that you are logged on as a member of the Schema Admins group).
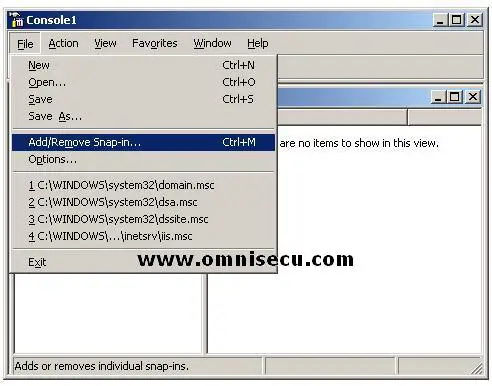
• To open "Active Directory Schema" snap-in, open mmc, choose menu "File", and then "Add/Remove snap-in)
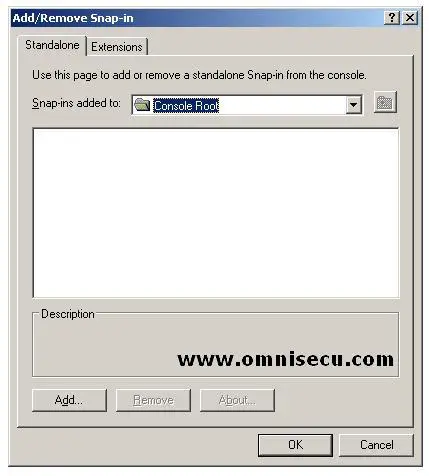
• Click "Add" button.
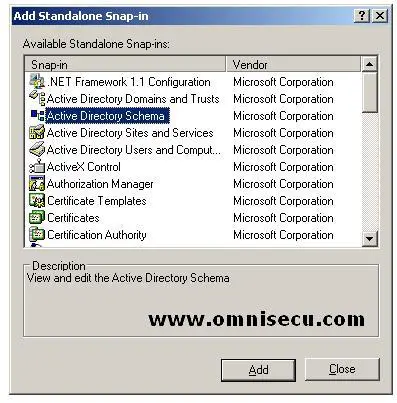
• Select "Active Directory Schema" from "Add Standalone Snap-in" and click "Add' button, and then click "OK" button.
• In console tree of the “Active Directory Schema” snap-in, right click the “Active Directory Schema” and select “Change Domain Controller”. Select the Domain controller to transfer the role.
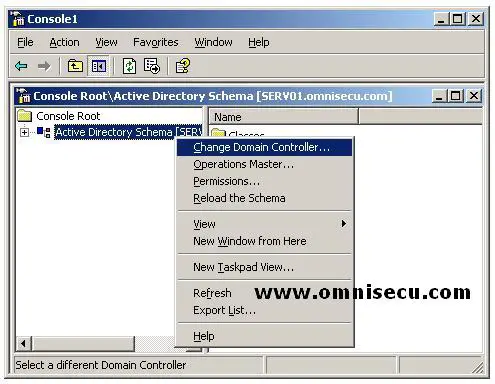
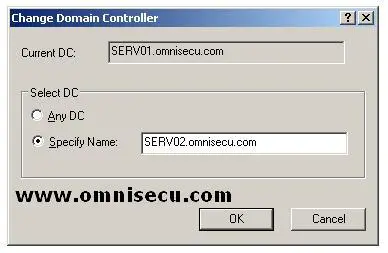
• Type the name of the new domain controller in the "Change Domain Controller" dialog box and click "OK" button as shown below.
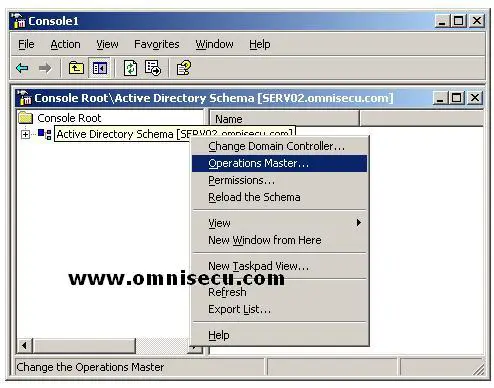
• Again right click the “Active Directory Schema” from the console tree and select the “Operations Master”.
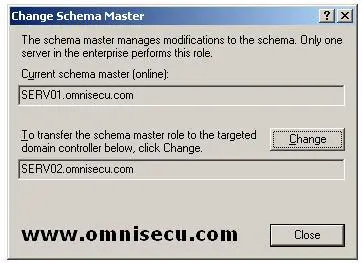
• Click “Change” in the "Change Schema Master" dialog box to change the Schema Operations Master to the new Domain Controller.
How to seize Operations Master (FSMO) roles using Ntdsutil tool
In some special cases, as shown below, we cannot trasfer the Operations Master (FSMO) roles from one Domain Controller to another Domain Controller .
• A Domain Controller that currently owns an Operations Master (FSMO) role is demoted forcefully by using the dcpromo /forceremoval command.
• The Operations
Master role holder is experiencing an operational error that prevents an
FSMO-dependent operation from completing successfully and that role
cannot be transferred.
• The operating system on the computer that originally owned a specific Operations Master (FSMO) role no longer exists.
The Ntdsutil tool allows you to transfer and seize operations master roles. When you use the Ntdsutil command-line tool to seize
an operations master role, the tool attempts a transfer from the
current role owner first. Then, if the existing operations master is
unavailable, it performs the seizure.
• Click Start, and then click Command Prompt.
• At the command prompt, type ntdsutil and hit ENTER.
• At the ntdsutil prompt, type roles and hit ENTER.
• At the fsmo maintenance prompt, type connections and hit ENTER.
• At the server connections prompt, type connect to server, followed by the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), and press ENTER.
• At the server connections prompt, type quit and hit ENTER.
• At the fsmo maintenance prompt, type one of the following and hit ENTER:
o seize schema master
o seize domain naming master
o seize RID master
o seize PDC
o seize infrastructure master
• At the fsmo maintenance prompt, type quit and hit ENTER.
• At the ntdsutil prompt, type quit and hit ENTER.
http://www.omnisecu.com/windows-2003/index.htm

0 comments
Post a Comment