Example Network and Perimeter Network Design
In this chapter, we will use the sample network shown in Figure 10.6 and outlined here:
-
The default gateway for all servers on the network services segment will be the IP address on the internal interface of the network services perimeter ISA firewall.
-
The default gateway for all hosts on the corporate network containing client systems is the IP address on the internal interface of the edge ISA firewall.
-
Client systems are configured with a routing table entry that forwards connections to network ID 10.0.0.0/24 to the IP address on the external interface of the network services perimeter ISA firewall.This is required because we do not have a LAN router in this configuration.
Figure 10.6: Our Sample Network
A Windows 2000 file server and an Exchange 2003 server are located on the network services segment.The Exchange server is also a domain controller, domain name system (DNS) server, Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) server, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, certificate server, and Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) server. We will create Access Rules that enable connections to all the network services on the Exchange server and to file shares on the file server.The file server will host the Firewall client installation files so that we can avoid allowing file sharing protocols to any portion of the ISA firewall’s local host network.The network services perimeter ISA firewall is already joined to the domain.
We will perform the following procedures:
-
Create an ISA firewall network representing the corporate network on the network services perimeter ISA firewall.
-
Create a network rule on the network services perimeter ISA firewall that sets a Route relationship between the corporate network and the network services network.
-
Create an intradomain communications Access Rule on the network services perimeter ISA firewall that allows corporate network hosts access to the domain controller on the services segment for intradomain communications, and a DNS Server Publishing Rule that enables the DNS application layer inspection filter.
-
Create Access Rules controlling outbound access from the network services segment on the perimeter ISA firewall.
-
Create network services Access Rules on the network services perimeter ISA fire-wall enabling client access to network services, such as Outlook Web Access (OWA), Outlook Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (STMP), Postoffice Protocol version 3 (POP3), and Internet Message Access Protocol version 4 (IMAP4), and file shares.
-
Create a routing table entry on the edge ISA firewall providing a path to the network services segment network ID.
-
Join the front-end ISA firewall to the domain.
-
Create a routing table entry on the network clients (required only if no LAN routers are installed) providing route information to reach the network services segment network ID.
-
Join the network clients to the domain.
-
Create a WPAD entry in DNS to enable autodiscovery for firewall and Web proxy clients.
-
Configure the Firewall client settings on the edge ISA firewall (including Web proxy client configuration).
-
Install the Firewall client share on the network services segment file server.
-
Install the Firewall client on the network clients.
-
Connect the corporate network clients to resources on the network services segment and the Internet.
Creating the ISA Representing the Corporate Network on the Network Services Perimeter
One of the most prevalent misconceptions regarding ISA firewall networks and how the ISA firewall sees the network world is how the ISA firewall deals with the default external network. Let’s set the record straight:The default external network on the ISA firewall is defined as any IP address that is not part of any other ISA firewall network defined on the ISA firewall.
This means you can configure any collection of IP addresses that aren’t part of another ISA firewall network to be part of a custom ISA firewall network.This includes the IP address(es) bound to the external interface of the ISA firewall (although the addresses on the external interface of the ISA firewall will always belong to the local host network).
This allows us to create a custom ISA firewall network that includes the IP addresses used on the corporate network between the edge ISA firewall and the network services perimeter ISA firewall.These addresses do not need to be part of the default external network, even though the corporate network is on the same network ID as the external interface of the ISA firewall.The term external interface only means that it’s the interface with the default gateway configured on it, which typically is the closest to the Internet.
| Note | Although the term external interface is used to denote the NIC that has the default gateway configured on it, the fact is that you can configure an ISA fire-wall that has no default gateway. This ISA firewall won’t be able to access the Internet, and hosts serviced by that ISA firewall won’t be able to access the Internet, but it illustrates that an ISA firewall does not require an external interface. |
The value in making the corporate network located between the edge ISA firewall and the network services perimeter ISA firewall a separate ISA firewall network is that you can control the routing relationship between that network and any other network defined on the ISA firewall.
In the example network used in this chapter, configuring a custom corporate ISA fire-wall network on the network perimeter services segment ISA firewall will enable us to create a Route relationship between the default internal network behind the back-end ISA firewall and the corporate network located between the edge ISA firewall and the network services ISA perimeter ISA firewall. We can also create Access Rules controlling traffic moving to and from any ISA firewall network.
Creating the Corpnet ISA Firewall Network
Perform the following steps on the network services perimeter ISA firewall to create the Corpnet ISA firewall network:
-
In the ISA firewall console, expand the server name and then expand the Configuration node. Click the Networks node.
-
On the Networks node, click the Networks tab in the Details pane. Click the Tasks tab in the Task pane and then click the Create a New Network link.
-
On the Welcome to the New Network Wizard page, enter a name for the network in the Network name text box. In this example, we’ll name the network Corpnet. Click Next.
-
On the Network Type page, select the Perimeter Network option and click Next.
-
On the Network Address page, click the Add button.
-
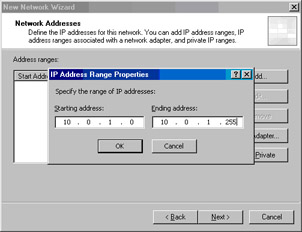
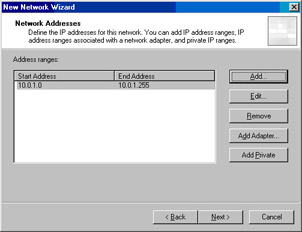
In the IP Address Range Properties dialog box, enter the Starting address and Ending address for the Corpnet ISA firewall network. In this example, we’ll enter 10.0.1.0 for the Starting address and 10.0.1.255 for the Ending address (see Figure 10.7). Note that you don’t have to include the entire network ID; you can include only the addresses that are actually in use on that network, or you can get even more granular and include only the addresses that you want to have a Route relationship with the default Internet network behind the network services perimeter ISA firewall so that you can later create another ISA firewall network representing other addresses on the corporate network that you want to create a NAT relationship with. Click OK, and then click Next. Figure 10.8 shows the results.
-
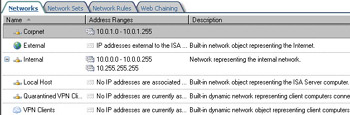
Click Finish on the Completing the New Network Wizard page. Figure 10.9 shows the results.





0 comments
Post a Comment